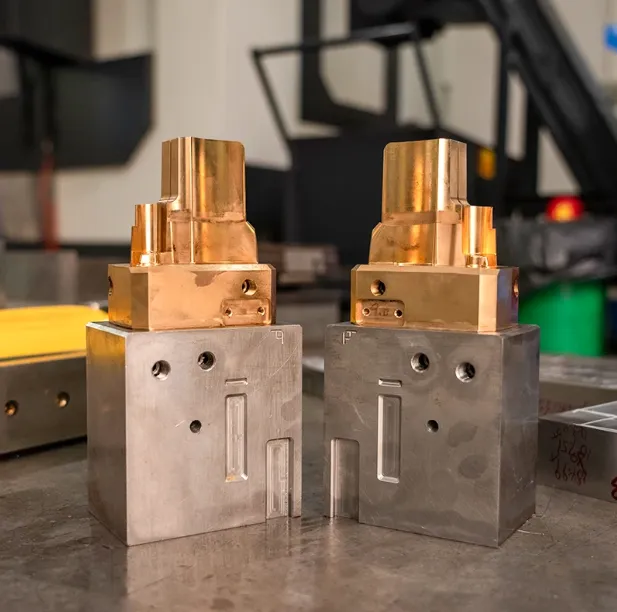
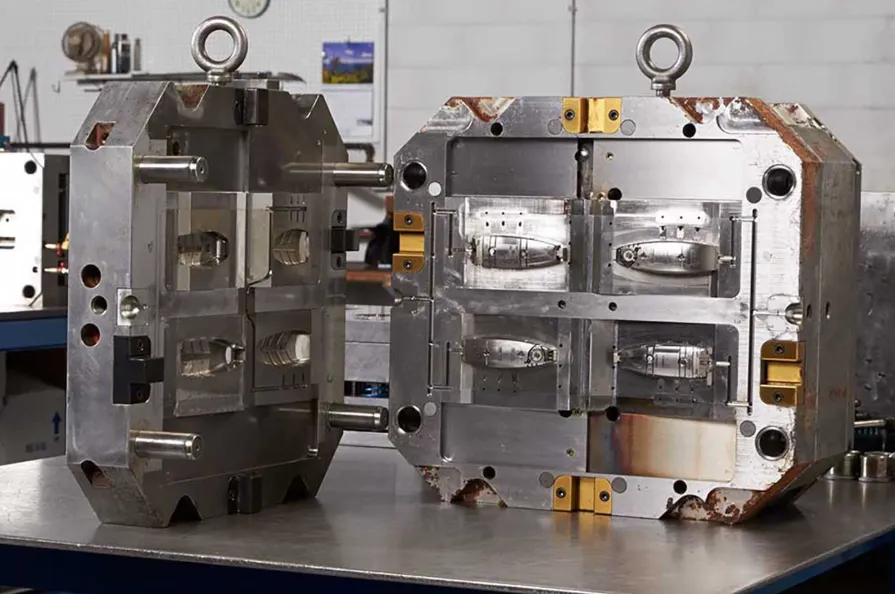
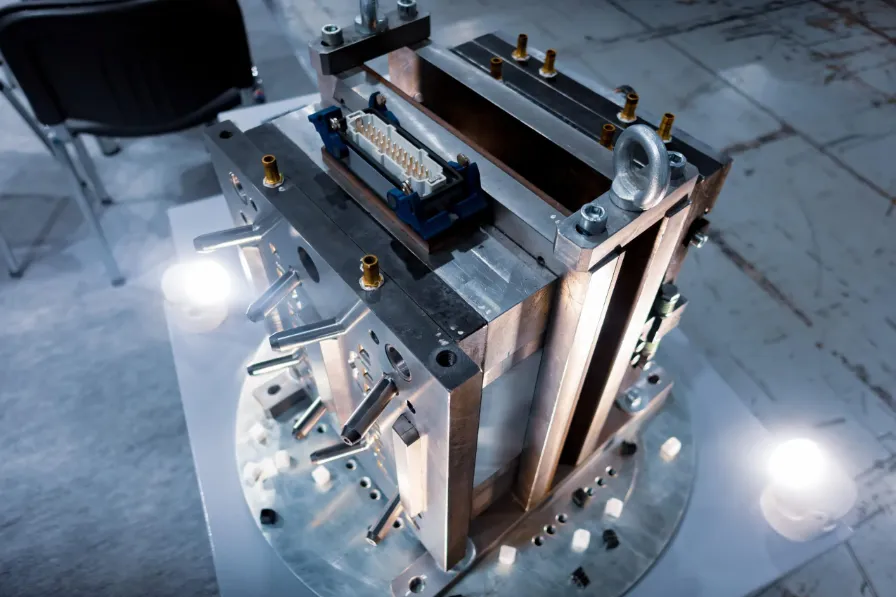
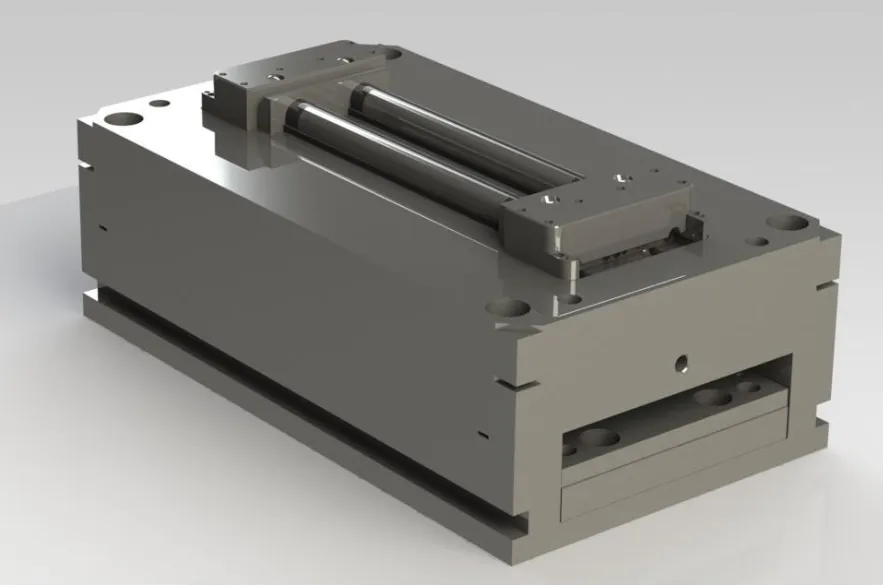
Injection molding stands as one of the most efficient and widely employed manufacturing processes today, revolutionizing the production of various plastic components and products. This article offers an in-depth exploration of injection molding, delving into its mechanisms, materials, advantages, applications, and future trends.
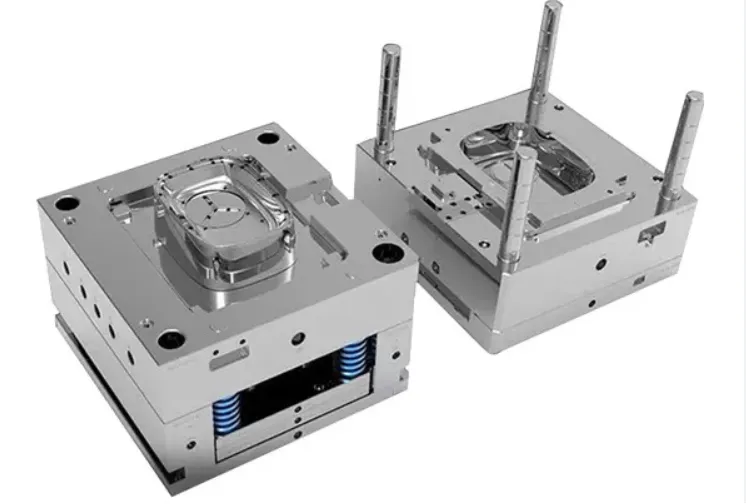

What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique used to create parts by injecting molten material, typically plastics or metals, into a pre-designed mold. The process involves several critical steps:
-
Mold Creation: The first step in injection molding is designing and fabricating the mold. Molds are usually made of two halves, which fit together to form a cavity that defines the shape of the final product. High-quality molds are crafted from durable materials, typically steel or aluminum, to withstand the high pressures of the injection process.
-
Injection of Material: Once the mold is prepared, plastic pellets are fed into a heated barrel where they are melted. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold cavity under high pressure using a reciprocating screw or plunger. This stage requires precise control to ensure that the material fills the entire cavity without any voids or defects.
-
Cooling and Solidification: After the mold is filled, the molten plastic is allowed to cool and solidify, taking on the shape of the mold. Cooling time is crucial, as it affects the characteristics of the final product and the overall cycle time of the injection molding process.
-
Ejection: Once the plastic has cooled sufficiently, the mold opens, and the newly formed part is ejected using ejector pins. The mold can then be closed again to repeat the process.
Key Materials Used in Injection Molding
Injection molding can accommodate a wide variety of materials, making it a versatile manufacturing process. The most commonly used materials include:
-
Thermoplastics: These are plastics that can be melted and remolded multiple times. Popular thermoplastics used in injection molding include polycarbonate (PC), polypropylene (PP), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS).
-
Thermosetting Plastics: Unlike thermoplastics, these materials undergo a chemical change when heated and cannot be remolded. Examples include epoxy resins and phenolic resins, which are often used for high-heat applications.
-
Metals: While less common, metals can also be injected using a process known as die-casting. This method allows the creation of intricate metal components used in various industries.
Advantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding offers numerous benefits, making it the preferred method in many manufacturing scenarios. Some key advantages include:
-
High Production Efficiency: The ability to produce large quantities of identical parts quickly and consistently makes injection molding an efficient manufacturing process. It is possible to achieve cycle times as short as 15 seconds for certain products.
-
Precision and Detail: Injection molds can be engineered to extremely tight tolerances, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries that may be challenging to achieve with other manufacturing processes.
-
Material Versatility: With a wide range of materials available, manufacturers can choose the most suitable option for their specific needs, whether it’s for flexibility, durability, or resistance to harsh environments.
-
Reduced Waste: The injection molding process generates less waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods, as excess material can often be recycled or reused.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial cost of creating high-quality molds can be significant, the long-term savings from mass production and reduced material waste contribute to lower overall production costs.
Applications of Injection Molding
The versatility of injection molding allows it to be used across countless industries, producing an extensive range of products. Some common applications include:
-
Consumer Products: Everyday items such as toys, kitchenware, and appliances are often produced via injection molding. The process enables manufacturers to create durable, attractive, and cost-effective consumer goods.
-
Automotive Parts: Injection molding is extensively utilized in the automotive industry for producing components like dashboards, interior panels, and exterior housings. The lightweight and efficient nature of molded plastics contributes to overall vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
-
Medical Devices: The healthcare sector relies on injection molding for the production of intricate medical devices and components, such as syringes, surgical instruments, and drug delivery systems. Strict regulatory standards necessitate precision and consistent quality standards in this field.
-
Electronics: Many electronic devices incorporate injection-molded parts, such as casings and connectors. The process allows for the manufacturing of complex shapes that provide protection and functionality for sensitive electronic components.
Future Trends in Injection Molding
As technology advances, the injection molding industry continues to evolve, integrating new trends and innovations. Some of the notable trends include:
-
Sustainability: Growing environmental concerns are driving the adoption of eco-friendly materials, such as bioplastics and recycled plastics, in the injection molding process. Companies are also seeking to implement more sustainable practices throughout the production cycle.
-
Smart Manufacturing: The incorporation of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence, into injection molding processes is enhancing efficiency and productivity. Smart factories enable real-time monitoring and data analysis, leading to improved quality control and reduced downtime.
-
3D Printing Integration: The synergy between injection molding and 3D printing is gaining traction, particularly in the prototyping phase. Designers can create rapid prototypes using 3D printing techniques before committing to expensive mold fabrication.
-
Advanced Mold Design: New technologies in mold design and manufacturing are allowing for more complex and innovative part designs, optimizing cooling systems, and improving cycle times.
-
Customization: As consumer preferences shift towards personalization, injection molding techniques are adapting to provide more customized products without significantly increasing production costs.
Conclusion
Injection molding is a dynamic and multifaceted manufacturing process that plays a critical role in modern production across various sectors. Its efficiency, precision, and versatility make it an ideal choice for producing everything from everyday consumer goods to advanced medical devices. As the industry advances and adapts to challenges, the future of injection molding holds promising potential for innovation and sustainability, paving the way for continued growth in manufacturing capabilities.