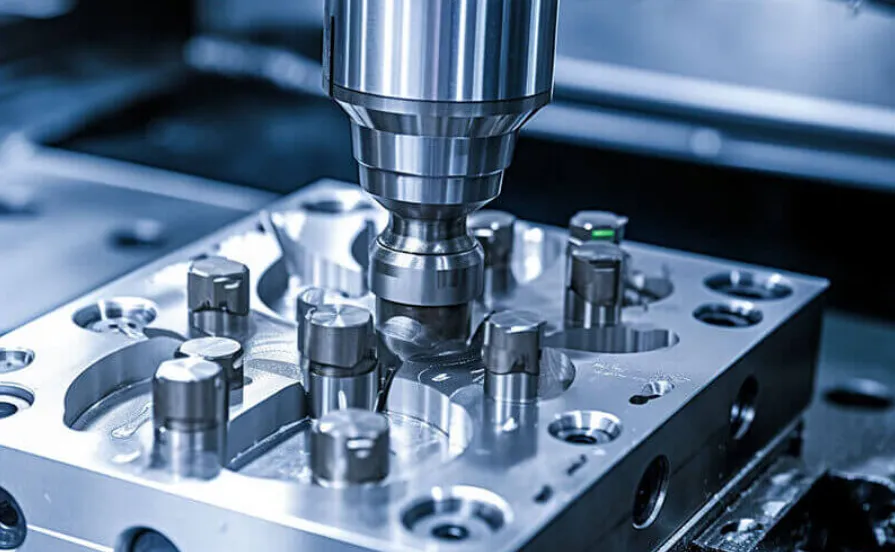
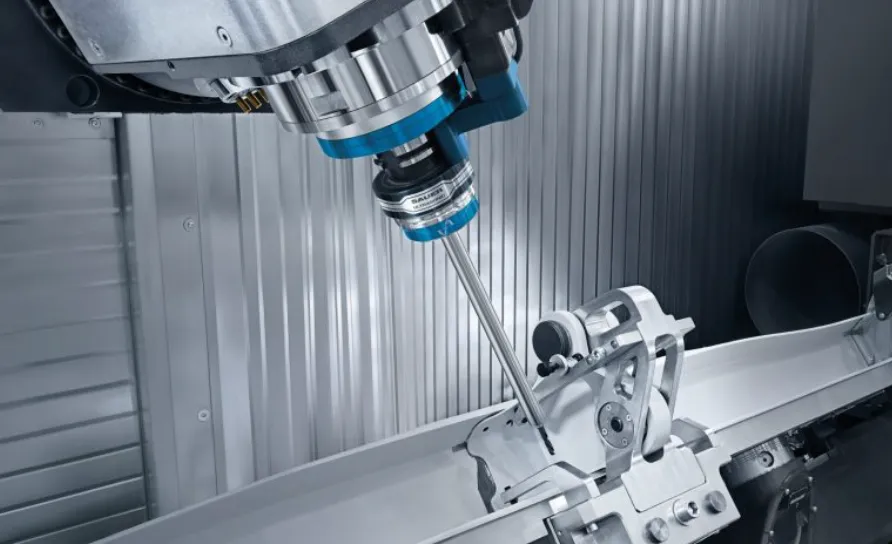
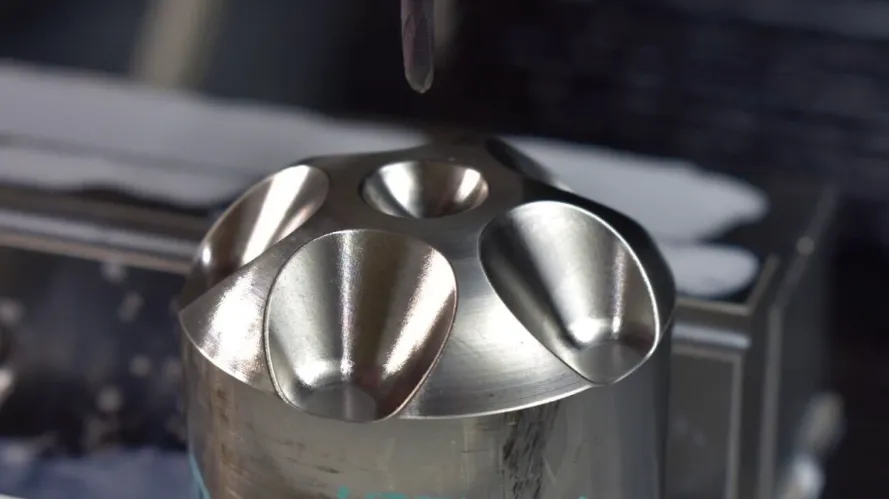
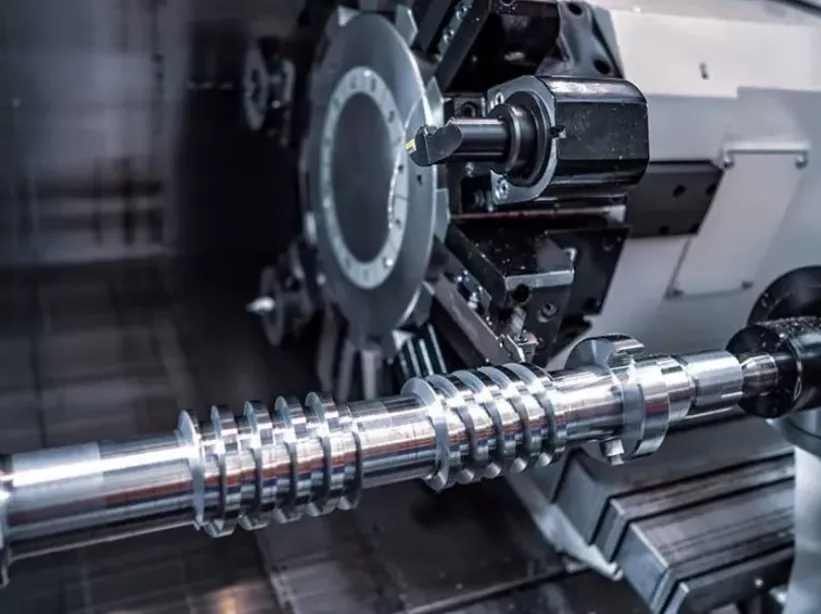
4-axis CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a sophisticated technique that enhances the capabilities of traditional 3-axis machining by adding an additional rotational axis. This innovation allows for more complex shapes and features to be machined with precision, making it a valuable tool in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing.

Understanding the 4-Axis System
In a standard 3-axis CNC machine, the cutting tool moves along three linear axes: X (left and right), Y (forward and backward), and Z (up and down). The introduction of a fourth axis—typically the A-axis—enables the workpiece to rotate around the X-axis, providing the ability to machine multiple sides of a part without the need to reposition it manually. This rotation significantly increases the machine’s capability to produce intricate geometries.
Benefits of 4-Axis CNC Machining
1. Increased Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of 4-axis CNC machining is the improvement in efficiency. The ability to machine multiple sides of a part in a single setup eliminates the need for multiple setups, reducing production time. This translates to shorter lead times and higher output for manufacturers.
2. Enhanced Precision
4-axis CNC machining contributes to enhanced precision and accuracy in production. The integrated A-axis allows for continuous control over the machining process, ensuring that toolpaths are executed with high precision. This is particularly beneficial for complex components requiring tight tolerances.
3. Complex Geometry Capabilities
The fourth axis enables the machining of complex geometries that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to achieve with a 3-axis machine. Features such as slots, holes, and intricate designs can be created with more ease, allowing for greater design flexibility.
4. Reduced Labor Costs
By minimizing the need for manual repositioning of parts and reducing setup times, 4-axis CNC machining can lower labor costs. Fewer setups mean that operators can manage more parts simultaneously, improving overall productivity.
Applications of 4-Axis CNC Machining
1. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, precision and reliability are paramount. 4-axis CNC machines are utilized to manufacture critical components such as turbine blades, housings, and brackets. The ability to produce complex shapes while maintaining high tolerances makes them indispensable in this field.
2. Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical industry often requires components with intricate geometries and precise specifications. 4-axis CNC machining is used to create surgical instruments, implants, and other medical devices that demand high quality and accuracy.
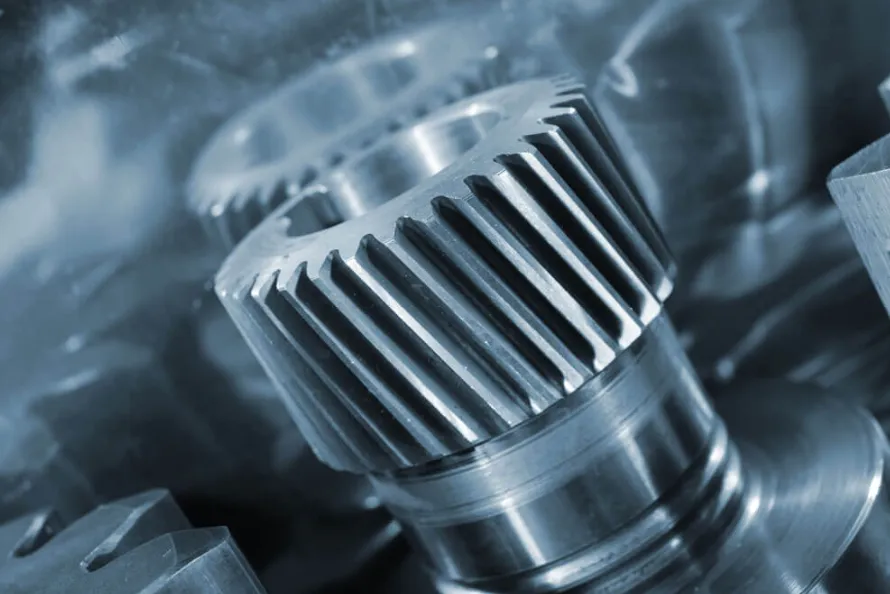
3. Automotive Sector
Automotive manufacturers benefit from 4-axis CNC machining for producing parts like engine components, brackets, and gear housings. The ability to quickly and accurately machine complex parts aids in meeting the high demands of modern automotive design.
4. Custom Fabrication
For industries requiring custom or small-batch productions, 4-axis CNC machining provides the flexibility to create tailored components efficiently. The technology can easily accommodate various materials, such as metals, plastics, and composites.
Challenges and Considerations
While 4-axis CNC machining offers numerous advantages, there are challenges associated with its implementation. The complexity of programming and the initial investment in advanced machinery can be substantial. Additionally, operators may require more training to manage the additional variables introduced by the fourth axis.
To address these challenges, manufacturers must carefully assess their production needs and consider investing in skilled personnel or specialized software to streamline the programming process.
In conclusion, 4-axis CNC machining represents a significant advancement in manufacturing technology, offering a myriad of benefits in terms of efficiency, precision, and complexity. As industries continue to evolve and demand more intricate and high-quality components, the role of 4-axis CNC machines will only become more critical in modern manufacturing processes.