In the world of woodworking, CNC machines for wood have revolutionized the way we create intricate designs, furniture, and decorative pieces. These machines combine the precision of computer-controlled technology with the artistry of woodworking, enabling craftsmen to push the boundaries of creativity. But what makes CNC machines for wood so special, and how do they work? Let’s explore their features, applications, and the technology that powers them.
What is a CNC Machine for Wood?
A CNC machine for wood is a computer-controlled cutting tool designed specifically for woodworking. It uses rotating cutting tools to carve, shape, and engrave wood with incredible precision. Whether you’re crafting a custom cabinet or a detailed sculpture, a CNC machine for wood can bring your vision to life.
Key Features
- High Precision: Achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.005 inches (0.127 mm).
- Versatility: Handles a wide range of wood types, including hardwood, plywood, and MDF.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly software and intuitive controls.
- Customization: Ideal for creating intricate designs and personalized pieces.
 How Does a CNC Machine for Wood Work?
How Does a CNC Machine for Wood Work?
The process of using a CNC machine for wood involves several steps, from design to finishing. Here’s a detailed look at how it works:
1. Design and CAD Modeling
The journey begins with a 3D CAD model, created using software like Fusion 360, SolidWorks, or AutoCAD. This digital blueprint is the foundation for everything that follows.
- Pro Tip: Use CAM software to optimize toolpaths and reduce machining time. Popular options include Vectric Aspire and Fusion 360.
2. Material Selection
The choice of wood depends on the project’s requirements. Common options include:
- Hardwood: Oak, maple, and walnut (durable, aesthetically pleasing).
- Plywood: Affordable, versatile, and easy to machine.
- MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard): Smooth surface, ideal for painting and finishing.
3. CNC Machining Process
The CNC machine uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Tool Selection: Choose the right tool for the job, such as end mills, ball nose cutters, or engraving bits.
- Cutting Parameters: Set spindle speed (RPM), feed rate (IPM), and depth of cut (DOC) based on wood type and tool type.
- Machining Operation: Execute the G-code program to perform the cutting operation.
Cutting Parameter Calculations
To optimize machining, use the following formulas:
- Spindle Speed (RPM):
 Where:
Where:
- CS = Cutting speed (SFM, surface feet per minute).
- D = Tool diameter (inches).
Scenario: For machining oak with a cutting speed of 800 SFM and a 0.25-inch end mill:

Warning: Exceeding recommended RPM can cause tool wear or burn marks on the wood. Always consult tool manufacturer guidelines.
- Feed Rate (IPM):

Where:
- FPT= Feed per tooth (inches).
- N= Number of teeth on the tool.
Scenario: For a 2-flute end mill at 12,223 RPM and 0.003 inches per tooth:
![]()
- Material Removal Rate (MRR):

Where:
- DOC = Depth of cut (inches).
- WOC = Width of cut (inches).
Scenario: For a 0.1-inch DOC and 0.25-inch WOC at 73.34 IPM:
![]()
Real-World G-Code Example
Here’s an example of a 3D carving operation using G-code, including tool compensation and spindle control:
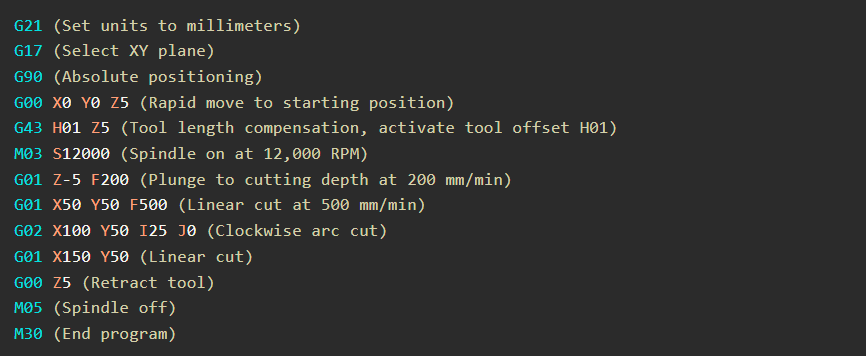
Key G-Code Explanations:
- G43 H01: Activates tool length compensation using offset H01.
- M03/M05: Turns spindle on/off.
- G02: Clockwise arc motion command.
4. Finishing and Inspection
After machining, the wood piece may undergo finishing processes like sanding, staining, or varnishing. Inspection tools like calipers or laser scanners ensure dimensional accuracy.
Why is a CNC Machine for Wood Essential?
1. Precision and Detail
CNC machines for wood enable the creation of intricate designs that would be impossible to achieve by hand. For example, a furniture maker used a CNC machine to produce a custom headboard with detailed floral patterns, reducing production time by 50%.
2. Efficiency and Speed
CNC machines can produce multiple identical pieces quickly and consistently. A 2021 study by Woodworking Network found that CNC machines increased production efficiency by 40% compared to manual methods.
3. Customization
CNC machines allow for easy customization, making them ideal for personalized projects like engraved signs or custom furniture.
Applications of CNC Machines for Wood
1. Furniture Making
CNC machines are used to create custom furniture pieces like tables, chairs, and cabinets. For example, IKEA uses CNC machines to produce high-precision components for its furniture.
2. Signage
CNC machines are essential for creating signs and displays. A 2023 case study by Signs of the Times highlighted how a company used CNC machining to reduce the production time of custom signs by 50%.
3. Artistic Creations
Artists use CNC machines to create intricate sculptures and decorative pieces. A wood sculptor reported a 30% increase in productivity after switching to a CNC machine.
Challenges and Limitations
1. High Initial Cost
CNC machines for wood can be expensive, with prices ranging from $10,000 to over $100,000. However, many businesses find the long-term savings in efficiency and material waste justify the investment.
2. Skilled Labor Required
Operating a CNC machine requires specialized training. A 2021 report by IndustryWeek highlighted a growing skills gap, with many companies struggling to find qualified operators.
3. Material Waste
CNC machining is a subtractive process, meaning it generates material waste. For complex designs, this can result in significant scrap.
The Future of CNC Machines for Wood
1. Smart Features
Future CNC machines could integrate IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities, enabling remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
2. Enhanced Software Integration
Improved software compatibility, including cloud-based CAM solutions, could streamline the design-to-production workflow.
3. Expanded Material Capabilities
Advances in tooling and spindle technology could allow CNC machines to handle harder materials, expanding their range of applications.
Conclusion
CNC machines for wood are transforming the woodworking industry, enabling craftsmen to achieve levels of precision and creativity that were once unimaginable. From furniture to art, these machines are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with wood. While challenges like high costs and skilled labor shortages persist, advancements in technology are paving the way for a smarter, more efficient future.
If you’re looking to elevate your woodworking projects, a CNC machine for wood is an investment worth considering. With its precision, versatility, and ease of use, it’s the perfect tool for bringing your ideas to life.
References
- Woodworking Network (2021) – Study on CNC machining in woodworking.
- Signs of the Times (2023) – Case study on CNC machining for signage.
- IndustryWeek (2021) – Article on the skills gap in CNC machining.
- Manufacturing Global (2020) – Analysis of cost savings with CNC machining.
- Aerospace Manufacturing and Design (2022) – Report on precision machining in aerospace.






