In today’s manufacturing landscape, precision tooling has become the critical differentiator between adequate and exceptional part quality. The industry has seen tooling tolerances shrink from ±0.1mm to ±0.005mm in just the past decade, with leading-edge applications now demanding ±0.001mm consistency in medical and aerospace components. This evolution has been driven by parallel advancements in cutting tool materials, machine tool rigidity, and metrology capabilities.
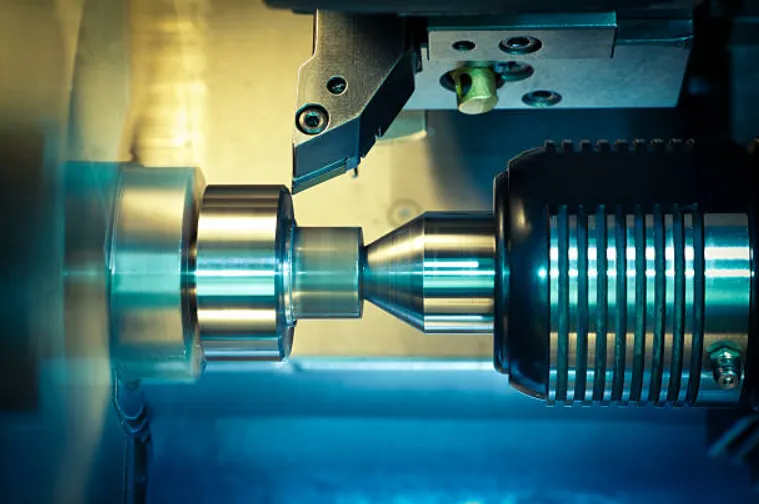 Carbide tooling now dominates the precision market, with submicron-grain tungsten carbide formulations offering 3-5 times the lifespan of conventional carbide in steel machining applications. Coatings have progressed equally dramatically – modern AlTiN (aluminum titanium nitride) nano-composite coatings maintain their edge integrity at temperatures exceeding 900°C, enabling high-speed machining of Inconel 718 at surface speeds of 120-150 m/min. For the most demanding applications, polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools deliver surface finishes below 0.2μm Ra in aluminum alloys while maintaining dimensional accuracy through 500,000+ cutting cycles.
Carbide tooling now dominates the precision market, with submicron-grain tungsten carbide formulations offering 3-5 times the lifespan of conventional carbide in steel machining applications. Coatings have progressed equally dramatically – modern AlTiN (aluminum titanium nitride) nano-composite coatings maintain their edge integrity at temperatures exceeding 900°C, enabling high-speed machining of Inconel 718 at surface speeds of 120-150 m/min. For the most demanding applications, polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools deliver surface finishes below 0.2μm Ra in aluminum alloys while maintaining dimensional accuracy through 500,000+ cutting cycles.
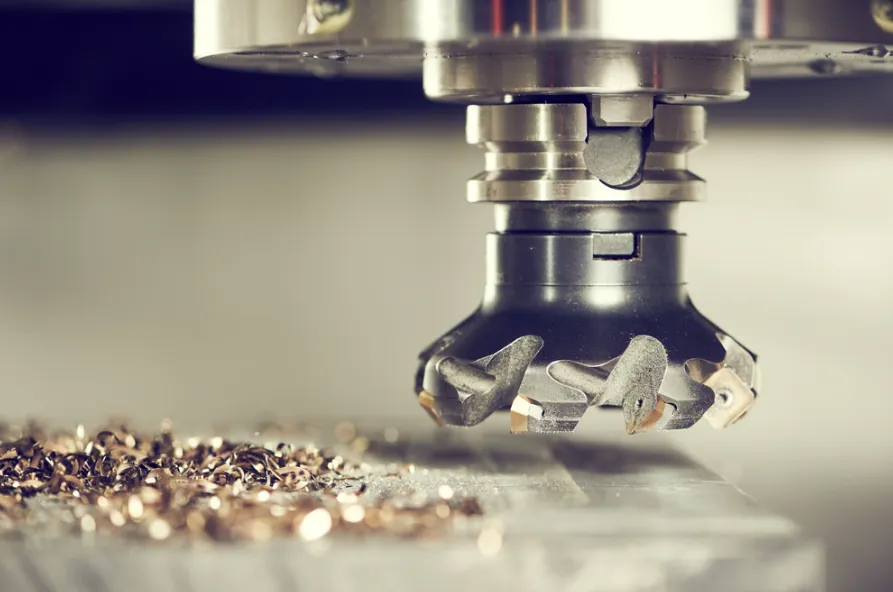

The medical device industry provides compelling examples of precision tooling’s capabilities. Orthopedic implant manufacturers now routinely machine cobalt-chrome femoral components using micro-grain carbide end mills as small as 0.3mm diameter. These tools, when paired with high-frequency spindle systems (60,000+ RPM), produce bone ingrowth surfaces with controlled porosity between 50-200μm – a specification impossible to achieve with conventional tooling. Similarly, cardiovascular stent manufacturing employs electrical discharge machining (EDM) electrodes ground to ±1μm tolerances to create intricate patterns in nitinol tubing.
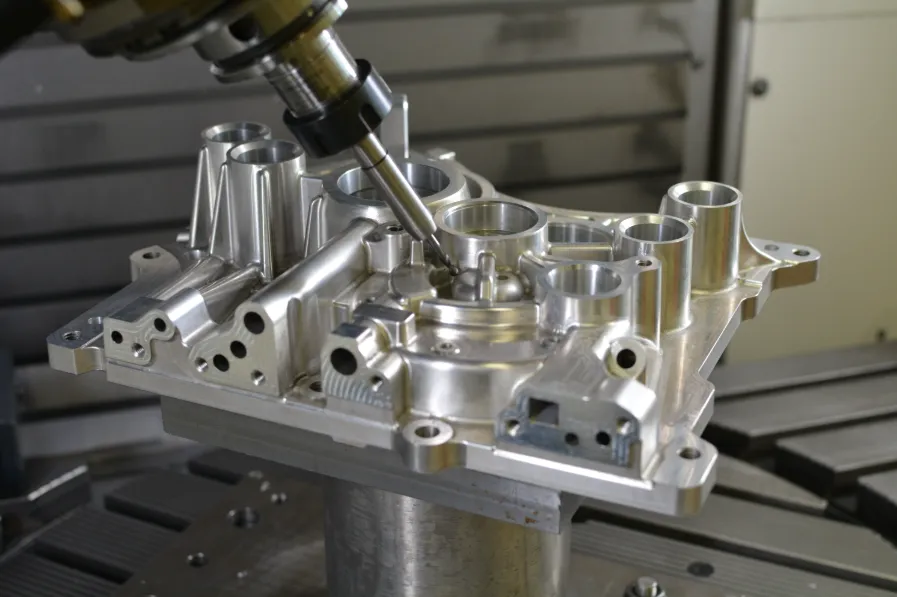

Recent innovations in tool presetting technology have significantly enhanced precision tooling’s effectiveness. Laser-based presetters like the Zoller Genius 3 measure cutting edge geometry to 1μm resolution while simultaneously detecting microscopic chips or coating defects. When integrated with modern CNC tool management systems, this data allows for automatic tool offset adjustments that compensate for predicted wear patterns, maintaining part tolerances through entire production runs.
The automotive sector’s transition to electric vehicles has created new precision tooling challenges. Machining copper motor components requires specialized tool geometries that prevent material adhesion while maintaining ±0.01mm positional accuracy at production rates exceeding 500 parts per shift. Solutions like diamond-coated tools with unique chipbreaker designs have emerged to meet these demands, reducing burr formation by 80% compared to conventional copper machining tools.
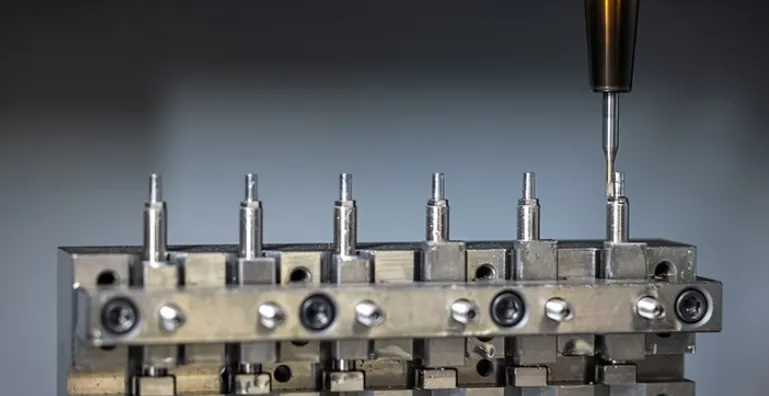
Quality assurance in precision tooling has evolved beyond simple dimensional checks. Advanced metrology systems now perform 3D cutting edge topography mapping, while acoustic emission sensors monitor tool condition in real-time. In one aerospace case study, implementing these technologies reduced scrap rates on titanium structural components from 3.2% to 0.4% while increasing tool life by 35%.
As additive manufacturing gains traction, precision tooling has adapted to meet hybrid manufacturing needs. Micro-milling tools designed specifically for finishing 3D-printed metal components can now achieve surface finishes below 0.8μm Ra while compensating for the unique residual stress patterns found in additively manufactured materials. This capability is revolutionizing mold and die production, where conformal cooling channels previously limited surface finish options.

The future of precision tooling lies in intelligent, connected systems. Emerging “smart tools” with embedded sensors provide real-time data on cutting forces, temperature, and vibration – information that adaptive control systems use to optimize machining parameters dynamically. This technological convergence promises to push manufacturing precision to new levels while dramatically improving process reliability across industries.




