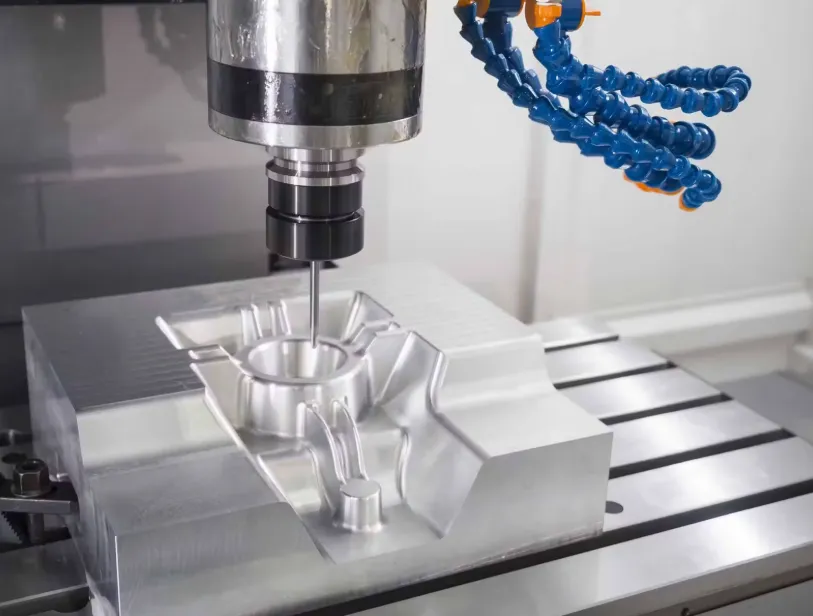
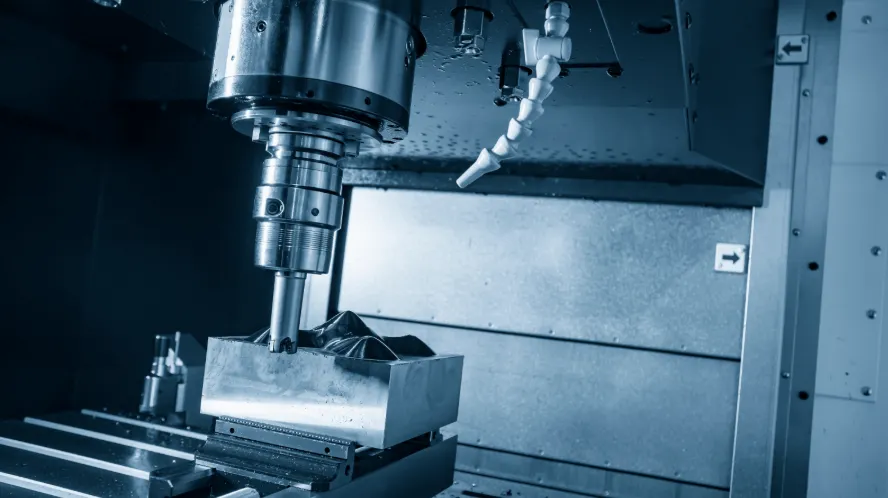
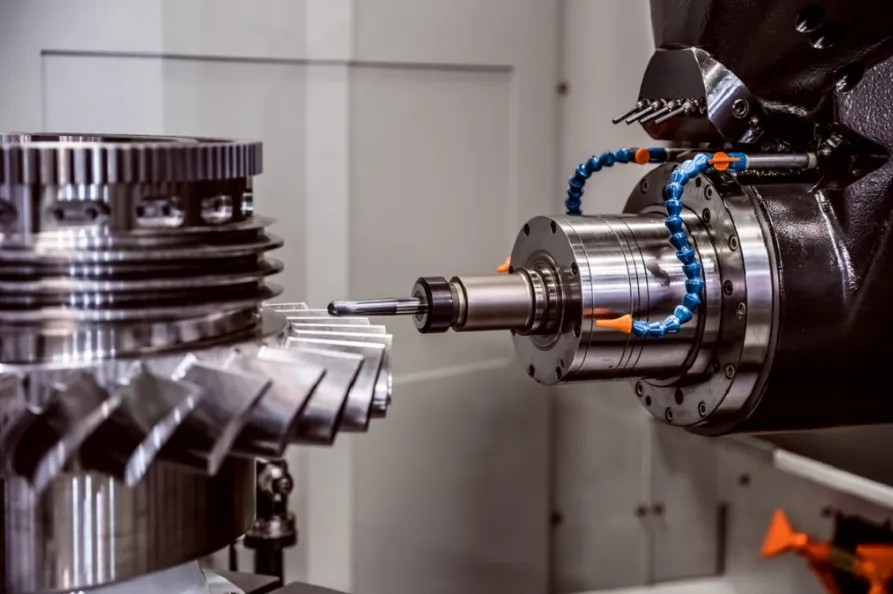
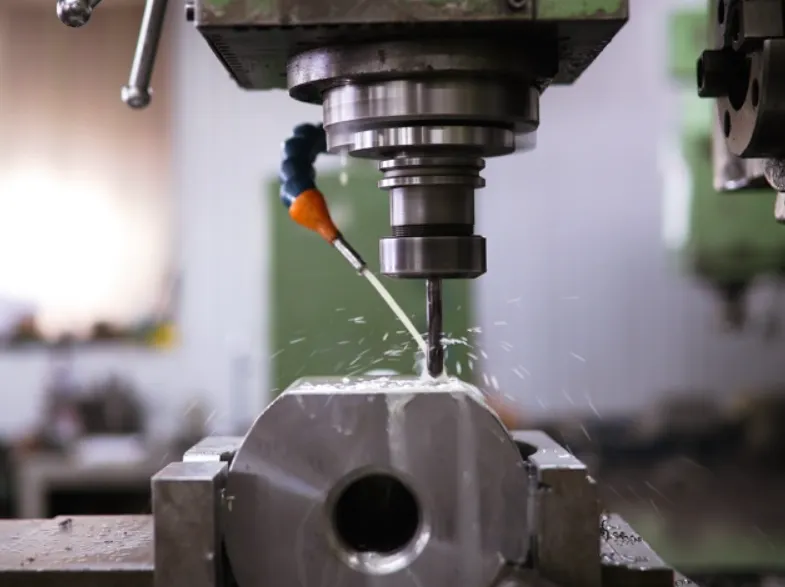
A milling machine is an essential tool in the fields of manufacturing and metalworking, used for removing material from a workpiece through the use of rotary cutters. It is vital for precision machining, allowing for the shaping and finishing of various materials. Understanding what a milling machine is, its types, working principles, and applications can provide insights into its significance in modern industrial practices.
Definition of a Milling Machine
A milling machine is a type of machine tool that operates by rotating a cutting tool (known as a milling cutter) to remove material from a stationary workpiece. Unlike lathes that rotate the workpiece and move a stationary cutting tool, milling machines utilize a rotating cutter that can move in multiple directions. This ability makes them versatile for producing complex shapes and features with high precision.

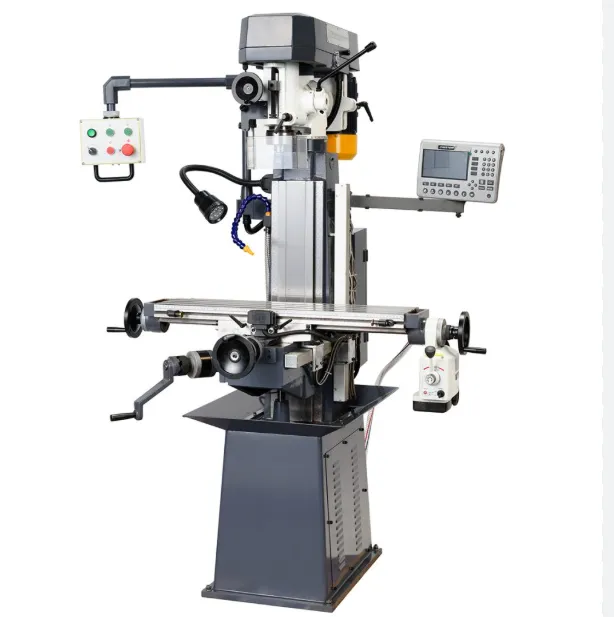
Main Types of Milling Machines
-
Vertical Milling Machine
- The spindle is oriented vertically, making it suitable for machining flat surfaces, grooves, and keyways.
- Simple structure and easy adjustments, ideal for small to medium-sized parts.
-
Horizontal Milling Machine
- Features a spindle that is parallel to the work surface; suitable for machining various flat surfaces and complex contours.
- Generally more efficient for larger, heavier workpieces.
-
Universal Milling Machine
- Combines features of both vertical and horizontal milling machines; the table can move in multiple directions.
- Highly versatile, suitable for a wide range of machining tasks.
-
CNC Milling Machine (Computer Numerical Control)
- Utilizes a computer control system to automate the milling process, achieving high precision and efficiency.
- Widely used in industries requiring complex parts, such as aerospace and automotive.
Working Principle of Milling Machines
Milling machines operate by rotating a cutting tool at high speeds while the workpiece is fed against it. The relative motion between the cutter and the workpiece allows for the removal of material:
- Cutting Speed and Feed Rate: These are crucial parameters affecting cutting efficiency and surface finish.
- Tool Selection: The choice of milling cutter depends on the material being machined and the required shape; materials include high-speed steel and carbide.
- Coolant Use: Applying coolant can help control the temperature generated by cutting and prolong tool life.
Applications of Milling Machines
Milling machines find applications across various industries, such as:
- Manufacturing: Used for producing parts and components in automotive and machinery.
- Aerospace: Critical in machining high-precision components for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Mold Making: Essential for creating molds used in plastic injection and metal casting.
- Medical Device Production: Used for precision machining of surgical instruments and medical equipment.
According to industry analysis by Fortune Business Insights, the global CNC machine market (including milling machines) was valued at approximately $63.22 billion in 2020, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% from 2021 to 2028.
Considerations for Using Milling Machines
- Safety Precautions: Always wear protective gear and avoid contact with rotating cutters.
- Proper Tool Selection: Choose the right cutter based on material and machining requirements.
- Maintenance of Parameters: Set spindle speed, feed rate, and cutting depth appropriately to reduce wear and improve finish.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure the machine is clean and lubricated, and replace worn parts timely.
- Workholding Solutions: Secure the workpiece properly to prevent movement during cutting.
How to Choose the Right Milling Machine
When selecting a milling machine, consider the following factors:
- Machining Needs: Identify the shapes, sizes, and precision requirements of the parts to be produced.
- Budget Considerations: Balance initial costs and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Brand and Support: Opt for well-known brands with solid technological backing and customer support.
- Compatibility: Ensure that tooling and fixturing solutions align with the selected milling machine.
Future Trends in Milling Machines
With growing automation and smart technology in manufacturing, milling machines are continually evolving. The integration of intelligent CNC systems enhances precision and efficiency. Moreover, the combination of additive manufacturing (3D printing) with traditional subtractive methods offers manufacturers greater flexibility and capability to meet specific production needs.
Conclusion
In summary, a milling machine is a multifaceted and indispensable tool in modern manufacturing. Its ability to perform various cutting operations with high precision makes it essential in numerous industries. By understanding its types, working principles, and applications, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting milling equipment. As technology advances, milling machines will continue to play a critical role in driving innovation and enhancing productivity in the manufacturing landscape.
If you have any further inquiries or need more information about milling machines, feel free to ask in the comments or explore additional resources on this topic. Best of luck in your manufacturing endeavors!●