A CNC router machine is a computer-controlled cutting system that precisely carves, cuts, and shapes various materials with exceptional accuracy. These automated cutting systems have revolutionized manufacturing processes across multiple industries by combining digital design capabilities with physical material processing.
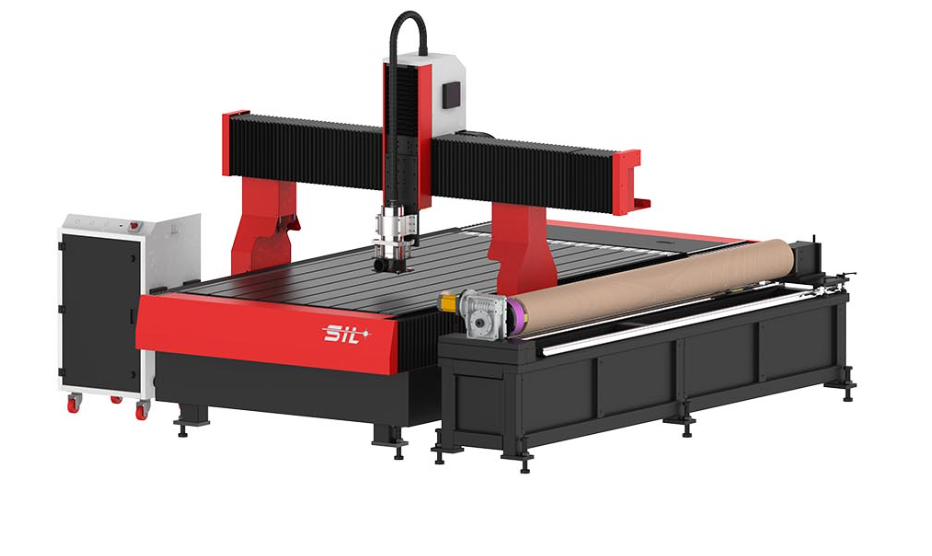 Core Components and Operation:
Core Components and Operation:
The machine consists of three primary systems working in coordination:
- Mechanical Structure – Built with rigid aluminum or steel frames supporting gantry systems that provide movement along X, Y, and Z axes
- Motion Control System – Uses servo or stepper motors with precision ball screws or rack-and-pinion drives
- Computer Control – Operates through specialized software that interprets CAD/CAM designs into machine movements
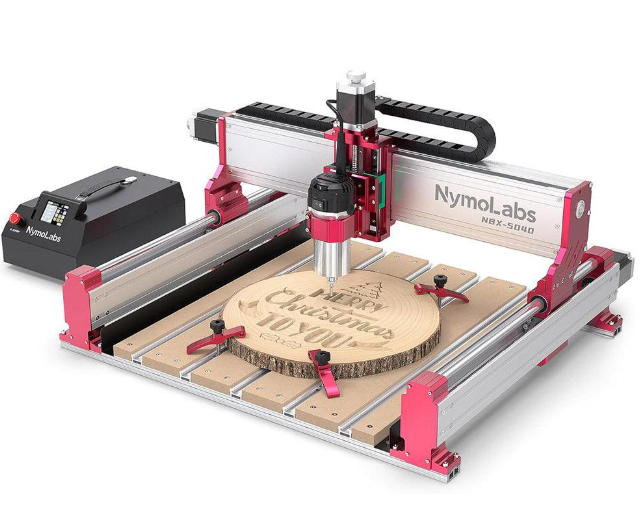
Technical Specifications:
Modern CNC routers feature:
- Cutting areas ranging from 4’x8′ (standard) up to 20’x100′ (industrial)
- Spindle power from 3HP (hobby) to 30HP (production)
- Positioning accuracy within ±0.001″ to ±0.005″
- Maximum feed rates between 400-1,200 inches per minute
Material Capabilities:
These versatile machines process numerous materials:
- Wood Products: Hardwoods, plywood, MDF, particleboard
- Plastics: Acrylic, PVC, polycarbonate, HDPE
- Metals: Aluminum, brass, copper (with appropriate tooling)
- Composites: Carbon fiber, fiberglass, laminates
Common Applications:
CNC routers serve diverse manufacturing needs:
- Sign Making: Cutting letters and dimensional signage
- Furniture Production: Creating cabinet components and decorative elements
- Aerospace: Manufacturing lightweight structural parts
- Prototyping: Developing product models and concept pieces
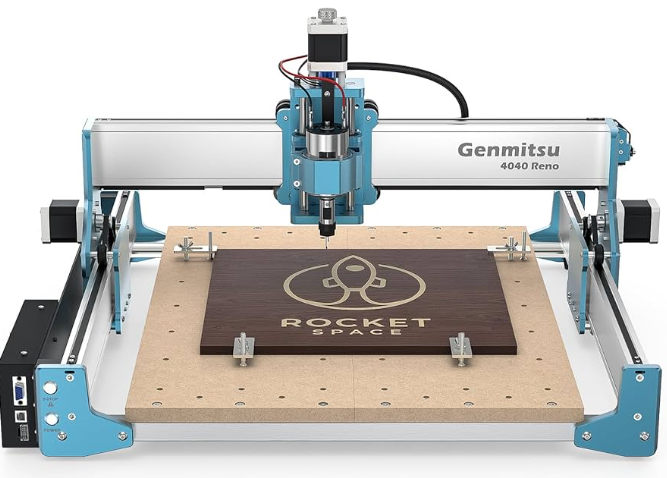
Control Systems:
Operation occurs through:
- G-code programming (standardized machine language)
- CAD/CAM software integration
- Touchscreen interfaces with visual previews
- Some models include conversational programming
Tooling Options:
Machines utilize various cutting tools:
- End mills (straight, spiral, compression)
- Ball nose cutters for 3D contouring
- V-bits for engraving
- Specialty bits for specific materials
Advanced Features:
Modern routers incorporate:
- Automatic tool changers (6-24 tool capacity)
- Vacuum hold-down systems
- Dust collection ports
- Laser positioning guides
- 4th axis rotary attachments
Industry Variations:
Different models serve specific sectors:
- Hobbyist: Smaller footprint, lower cost
- Industrial: Heavy-duty construction for production
- Plasma: For metal cutting applications
- 3D: For complex dimensional carving

Safety Systems:
Built-in protections include:
- Emergency stop buttons
- Limit switches
- Spindle overload protection
- Enclosure interlocks
CNC router technology continues evolving with improved precision, faster processing speeds, and enhanced software integration, maintaining its position as an essential manufacturing tool for both small shops and large production facilities.




